Pes Planus Explained
Overview

A fallen arch is when an arch, even one that has always been flat, has gotten flatter. There are several reasons for this. The bottom of heel tilts toward the inside, making the inside of the ankle appear convex or bowed. The feet often appear to be rotates outward, like a duck. And the arch sags toward the ground. Fallen arches? are more than just flat feet. Having flat feet is not a disease. It is a description of the shape of the foot. Most flat feet have been like that all of the person?s life. Usually they are not painful.
Causes
Infants and young children naturally have flat feet. The arch should develop over time. Sometimes, the arch does not develop. It is not always clear why this happens. Flat feet may develop because of ruptured or damaged tendon that supports the arch, medical conditions that affect muscles or nerves in the foot, degenerative changes in certain foot joints, Ligament damage in the foot.
Symptoms
A symptom is something the patient feels and reports, while a sign is something other people, including the doctor may detect. An example of a symptom may be pain in the ankle, while a sign may be a swelling. Symptoms may vary and generally depend on the severity of the condition. Some have an uneven distribution of bodyweight and find that the heel of their shoes wears out more rapidly and more on one side than the other. The most common signs or symptoms of flat feet are pain in the ankle (inner side), there may also be swelling of the foot in general, swelling in the arch of the foot, the calf, knee, the hip, the back, the general lower leg area. People with flat feet may also experience stiffness in one or both feet. One or both feet may be flat on the ground (either no arch, or very slight arch). Shoes may wear unevenly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of flat feet or fallen arches can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following. Clinical assessment involving visual gait assessment, as well as biomechanical assessment. A detailed family and medical history. A pain history assessment determining the location of painful symptoms. Physical palpation of the feet and painful areas. Imaging such as MRI or x-ray can be used by your practitioner to assist in the diagnosis.
no-foot-pain.com
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of flat feet really depends on how far the damage has progressed. Conservative treatments often include immobilization (often by cast or brace) to reduce inflammation. Your doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory medication (like ibuprofen) to get your inflamed tendon to calm down a bit. Orthotics can also offer significant relief. If these treatments fail to significantly improve symptoms, then surgery may be your best option to get the structure of your body back where it needs to be. Your podiatrist can discuss surgical options with you in great depth.
Surgical Treatment

Generally one of the following procedures is used to surgically repair a flat foot or fallen arch. Arthrodesis. One or more of your bones in the foot or ankle are fused together. Osteotomy. Correcting alignment by cutting and reshaping a bone. Excision. Removing a bone or a bone spur. Synovectomy. Cleaning the sheath that covers the tendon. Tendon transfer. Using a piece of one tendon to lengthen or replace another. Arthroereisis. placing a small device in the subtalar joint to limit motion. For most people, treatment is successful, regardless of the cause, although the cause does does play a major role in determining your prognosis. Some causes do not need treatment, while others require a surgical fix.
Prevention
It?s time to take a long hard look at what?s in your closet. Now is the time to toss out shoes that are well worn. You also need to say good-bye to thin-soled shoes that offer zero arch support. If you?re overweight, fallen arches may be a sign the universe is trying to tell you something. You need to lose weight, and odds are, fallen arches are but one of many physical discomforts you are experiencing.

A fallen arch is when an arch, even one that has always been flat, has gotten flatter. There are several reasons for this. The bottom of heel tilts toward the inside, making the inside of the ankle appear convex or bowed. The feet often appear to be rotates outward, like a duck. And the arch sags toward the ground. Fallen arches? are more than just flat feet. Having flat feet is not a disease. It is a description of the shape of the foot. Most flat feet have been like that all of the person?s life. Usually they are not painful.
Causes
Infants and young children naturally have flat feet. The arch should develop over time. Sometimes, the arch does not develop. It is not always clear why this happens. Flat feet may develop because of ruptured or damaged tendon that supports the arch, medical conditions that affect muscles or nerves in the foot, degenerative changes in certain foot joints, Ligament damage in the foot.
Symptoms
A symptom is something the patient feels and reports, while a sign is something other people, including the doctor may detect. An example of a symptom may be pain in the ankle, while a sign may be a swelling. Symptoms may vary and generally depend on the severity of the condition. Some have an uneven distribution of bodyweight and find that the heel of their shoes wears out more rapidly and more on one side than the other. The most common signs or symptoms of flat feet are pain in the ankle (inner side), there may also be swelling of the foot in general, swelling in the arch of the foot, the calf, knee, the hip, the back, the general lower leg area. People with flat feet may also experience stiffness in one or both feet. One or both feet may be flat on the ground (either no arch, or very slight arch). Shoes may wear unevenly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of flat feet or fallen arches can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following. Clinical assessment involving visual gait assessment, as well as biomechanical assessment. A detailed family and medical history. A pain history assessment determining the location of painful symptoms. Physical palpation of the feet and painful areas. Imaging such as MRI or x-ray can be used by your practitioner to assist in the diagnosis.
no-foot-pain.com
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of flat feet really depends on how far the damage has progressed. Conservative treatments often include immobilization (often by cast or brace) to reduce inflammation. Your doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory medication (like ibuprofen) to get your inflamed tendon to calm down a bit. Orthotics can also offer significant relief. If these treatments fail to significantly improve symptoms, then surgery may be your best option to get the structure of your body back where it needs to be. Your podiatrist can discuss surgical options with you in great depth.
Surgical Treatment

Generally one of the following procedures is used to surgically repair a flat foot or fallen arch. Arthrodesis. One or more of your bones in the foot or ankle are fused together. Osteotomy. Correcting alignment by cutting and reshaping a bone. Excision. Removing a bone or a bone spur. Synovectomy. Cleaning the sheath that covers the tendon. Tendon transfer. Using a piece of one tendon to lengthen or replace another. Arthroereisis. placing a small device in the subtalar joint to limit motion. For most people, treatment is successful, regardless of the cause, although the cause does does play a major role in determining your prognosis. Some causes do not need treatment, while others require a surgical fix.
Prevention
It?s time to take a long hard look at what?s in your closet. Now is the time to toss out shoes that are well worn. You also need to say good-bye to thin-soled shoes that offer zero arch support. If you?re overweight, fallen arches may be a sign the universe is trying to tell you something. You need to lose weight, and odds are, fallen arches are but one of many physical discomforts you are experiencing.
Leg Length Discrepancy Shoe Inserts
Overview
Surgeries to lengthen a leg are generally only performed when there is a difference in leg length of greater than four centimeters. These types of surgeries can be more difficult and have more complications, such as infections, delayed healing, dislocations, and high blood pressure. In a several step process, bone lengthening surgeries involve cutting a bone in two in order to allow new bone growth to occur. After the bone is cut, a special apparatus is worn with pins that will pull the bone apart at approximately one millimeter per day. This causes osteogenesis, or new bone growth, in between the cut bone segments. A cast or brace may be required for several months after surgery to allow the new bone growth to harden and provide extra support.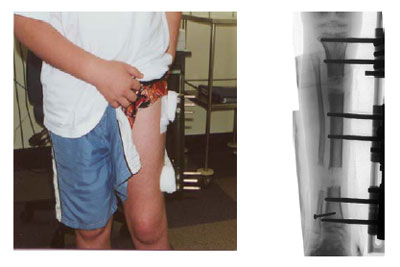
Causes
Some limb-length differences are caused by actual anatomic differences from one side to the other (referred to as structural causes). The femur is longer (or shorter) or the cartilage between the femur and tibia is thicker (or thinner) on one side. There could be actual deformities in one femur or hip joint contributing to leg length differences from side to side. Even a small structural difference can amount to significant changes in the anatomy of the limb. A past history of leg fracture, developmental hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), short neck of the femur, or coxa vara can also lead to placement of the femoral head in the hip socket that is offset. The end-result can be a limb-length difference and early degenerative arthritis of the hip.
Symptoms
Patients with significant lower limb length discrepancies may walk with a limp, have the appearance of a curved spine (non-structural scoliosis), and experience back pain or fatigue. In addition, clothes may not fit right.
Diagnosis
A systematic and well organized approach should be used in the diagnosis of LLD to ensure all relevant factors are considered and no clues are overlooked which could explain the difference. To determine the asymmetry a patient should be evaluated whilst standing and walking. During the process special care should be used to note the extent of pelvic shift from side to side and deviation along the plane of the front or leading leg as well as the traverse deviation of the back leg and abnormal curvature of the spine. Dynamic gait analysis should be conducted during waling where observation of movement on the sagittal, frontal and transverse planes should be noted. Also observe head, neck and shoulder movements for any tilting.
Non Surgical Treatment
Whether or not treatment should be pursued depends on the amount of discrepancy. In general, no treatment (other than a heel life, if desired) should be considered for discrepancies under two centimeters. If the discrepancy measures between two and five centimeters, one might consider a procedure to equalize leg length. Usually, this would involve closure of the growth plate on the long side, thereby allowing the short side to catch up; shortening the long leg; or possibly lengthening the short leg.

deelsonheels
Surgical Treatment
Large leg length inequalities can be treated by staged lengthenings or by simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Additionally, lengthenings can be combined with appropriately timed epiphysiodesis in an effort to produce leg length equality. Staged lengthenings are often used for congenital deficiencies such as fibular hemimelia, in which 15 cm or more may be needed to produce leg length equality. We typically plan for the final lengthening to be completed by age 13 or 14 years, and allow at least 3 years between lengthenings. Lengthening of both the tibia and femur simultaneously requires aggressive therapy and treatment of soft tissue contractures. Curran et al[57] reported the need for surgical release of soft tissue contractures in 3 of 8 patients treated with simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Lengthening over an IM nail can be done in an effort to decrease the amount of time the fixator needs to be worn and to prevent angular malalignment. This technique requires that the patient be skeletally mature and it carries a higher risk of osteomyelitis (up to 15%). Additionally, if premature consolidation occurs, a repeat corticotomy is more difficult.
Surgeries to lengthen a leg are generally only performed when there is a difference in leg length of greater than four centimeters. These types of surgeries can be more difficult and have more complications, such as infections, delayed healing, dislocations, and high blood pressure. In a several step process, bone lengthening surgeries involve cutting a bone in two in order to allow new bone growth to occur. After the bone is cut, a special apparatus is worn with pins that will pull the bone apart at approximately one millimeter per day. This causes osteogenesis, or new bone growth, in between the cut bone segments. A cast or brace may be required for several months after surgery to allow the new bone growth to harden and provide extra support.

Causes
Some limb-length differences are caused by actual anatomic differences from one side to the other (referred to as structural causes). The femur is longer (or shorter) or the cartilage between the femur and tibia is thicker (or thinner) on one side. There could be actual deformities in one femur or hip joint contributing to leg length differences from side to side. Even a small structural difference can amount to significant changes in the anatomy of the limb. A past history of leg fracture, developmental hip dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), short neck of the femur, or coxa vara can also lead to placement of the femoral head in the hip socket that is offset. The end-result can be a limb-length difference and early degenerative arthritis of the hip.
Symptoms
Patients with significant lower limb length discrepancies may walk with a limp, have the appearance of a curved spine (non-structural scoliosis), and experience back pain or fatigue. In addition, clothes may not fit right.
Diagnosis
A systematic and well organized approach should be used in the diagnosis of LLD to ensure all relevant factors are considered and no clues are overlooked which could explain the difference. To determine the asymmetry a patient should be evaluated whilst standing and walking. During the process special care should be used to note the extent of pelvic shift from side to side and deviation along the plane of the front or leading leg as well as the traverse deviation of the back leg and abnormal curvature of the spine. Dynamic gait analysis should be conducted during waling where observation of movement on the sagittal, frontal and transverse planes should be noted. Also observe head, neck and shoulder movements for any tilting.
Non Surgical Treatment
Whether or not treatment should be pursued depends on the amount of discrepancy. In general, no treatment (other than a heel life, if desired) should be considered for discrepancies under two centimeters. If the discrepancy measures between two and five centimeters, one might consider a procedure to equalize leg length. Usually, this would involve closure of the growth plate on the long side, thereby allowing the short side to catch up; shortening the long leg; or possibly lengthening the short leg.

deelsonheels
Surgical Treatment
Large leg length inequalities can be treated by staged lengthenings or by simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Additionally, lengthenings can be combined with appropriately timed epiphysiodesis in an effort to produce leg length equality. Staged lengthenings are often used for congenital deficiencies such as fibular hemimelia, in which 15 cm or more may be needed to produce leg length equality. We typically plan for the final lengthening to be completed by age 13 or 14 years, and allow at least 3 years between lengthenings. Lengthening of both the tibia and femur simultaneously requires aggressive therapy and treatment of soft tissue contractures. Curran et al[57] reported the need for surgical release of soft tissue contractures in 3 of 8 patients treated with simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Lengthening over an IM nail can be done in an effort to decrease the amount of time the fixator needs to be worn and to prevent angular malalignment. This technique requires that the patient be skeletally mature and it carries a higher risk of osteomyelitis (up to 15%). Additionally, if premature consolidation occurs, a repeat corticotomy is more difficult.
All You Want To Know About
Overview

Every time you take a step, one of your heels has to support the whole weight of your body. As you move, the load is equal to 20 times your own body weight. The load is softened by a pillow of fat under the heel and a large sinew or ligament (the fibrous tissue that joins muscle and bone together) under the sole of the foot. This sinew is called the plantar fascia and it pulls the heel bone forward (in opposition to the Achilles tendon, which pulls it backwards). If an athlete does not warm up properly or a person with a sedentary job exercises heavily during the weekends, they might overload the muscles of the calf or strain the Achilles tendon, which joins these muscles to the heel bone. When overloaded the tendon becomes tight and painfully inflamed, which places extra strain on the plantar fascia and muscles in the soles of the foot. The strained plantar fascia becomes inflamed and may even develop tiny cracks. This is known as plantar fasciitis. Every time you sit down, sleep or otherwise rest your legs, the muscles of the sole of the foot will contract in an attempt to protect the damaged sinew. The pain in the heel will then no longer be felt. But when you get up again and put weight on the foot, the foot and ankle may feel stiff (because of the inflammation) and the pain will return either at the back of the heel or on the soles of the feet. When you start to move, the plantar fascia may crack even more causing a vicious cycle of damage and pain. Inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon (at the back of the heel) or the plantar fascia (under the heel) join the heel bone (a bone known as the Calcaneum) stimulates cells that form bone to deposit bone in this area, eventually leading to the build up of a bony prominence on the heel bone called a calcaneal spur. But it's not the spur itself that causes the pain. The spur is a sign of chronic inflammation in the connective tissues, which is the result of a prolonged overload. It should also be pointed out that heel spurs can occur on their own, without plantar fasciitis or pain, or may be linked to some types of arthritis (inflammation of the joints). And plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis don't necessarily lead to spur formation.
Causes
The plantar fascia spans the long arch of the foot from the heel to the base of the toes, where it blends with the soft tissues, then anchoring to the base of the toes. Plantar Fascia. The plantar fascia is a common cause of heel pain. As the bony attachment at the heel is considered the plantar fascia?s ?weak spot?, the patient will present with pain at the heel, mainly on the inside. The most common predisposing factor to this condition is the pronating (flattening feet) - 52% - whilst there is also some evidence that a very high arch, in a rigid foot (pes cavus), also was reasonably common - 42%.
Symptoms
Plantar fascia usually causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel although some people have heel spurs and suffer no symptoms at all. Occasionally, heel pain is also associated with other medical disorders such as arthritis (inflammation of the joint), bursitis (inflammation of the tissues around the joint). Those who have symptoms may experience ?First step? pain (stone bruise sensation) after getting out of bed or sitting for a period of time. Pain after driving. Pain on the bottom of your heel. Deep aching pain. Pain can be worse when barefoot.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel pain often goes away on its own with home care. For heel pain that isn't severe, try the following. Rest. If possible, avoid activities that put stress on your heels, such as running, standing for long periods or walking on hard surfaces. Ice. Place an ice pack or bag of frozen peas on your heel for 15 to 20 minutes three times a day. New shoes. Be sure your shoes fit properly and provide plenty of support. If you're an athlete, choose shoes appropriate for your sport and replace them regularly. Foot supports. Heel cups or wedges that you buy in the drugstore often provide relief. Custom-made orthotics usually aren't needed for heel problems. Over-the-counter pain medications. Aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) can reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
deelsonheels
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.

Every time you take a step, one of your heels has to support the whole weight of your body. As you move, the load is equal to 20 times your own body weight. The load is softened by a pillow of fat under the heel and a large sinew or ligament (the fibrous tissue that joins muscle and bone together) under the sole of the foot. This sinew is called the plantar fascia and it pulls the heel bone forward (in opposition to the Achilles tendon, which pulls it backwards). If an athlete does not warm up properly or a person with a sedentary job exercises heavily during the weekends, they might overload the muscles of the calf or strain the Achilles tendon, which joins these muscles to the heel bone. When overloaded the tendon becomes tight and painfully inflamed, which places extra strain on the plantar fascia and muscles in the soles of the foot. The strained plantar fascia becomes inflamed and may even develop tiny cracks. This is known as plantar fasciitis. Every time you sit down, sleep or otherwise rest your legs, the muscles of the sole of the foot will contract in an attempt to protect the damaged sinew. The pain in the heel will then no longer be felt. But when you get up again and put weight on the foot, the foot and ankle may feel stiff (because of the inflammation) and the pain will return either at the back of the heel or on the soles of the feet. When you start to move, the plantar fascia may crack even more causing a vicious cycle of damage and pain. Inflammation at the point where the Achilles tendon (at the back of the heel) or the plantar fascia (under the heel) join the heel bone (a bone known as the Calcaneum) stimulates cells that form bone to deposit bone in this area, eventually leading to the build up of a bony prominence on the heel bone called a calcaneal spur. But it's not the spur itself that causes the pain. The spur is a sign of chronic inflammation in the connective tissues, which is the result of a prolonged overload. It should also be pointed out that heel spurs can occur on their own, without plantar fasciitis or pain, or may be linked to some types of arthritis (inflammation of the joints). And plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis don't necessarily lead to spur formation.
Causes
The plantar fascia spans the long arch of the foot from the heel to the base of the toes, where it blends with the soft tissues, then anchoring to the base of the toes. Plantar Fascia. The plantar fascia is a common cause of heel pain. As the bony attachment at the heel is considered the plantar fascia?s ?weak spot?, the patient will present with pain at the heel, mainly on the inside. The most common predisposing factor to this condition is the pronating (flattening feet) - 52% - whilst there is also some evidence that a very high arch, in a rigid foot (pes cavus), also was reasonably common - 42%.
Symptoms
Plantar fascia usually causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel although some people have heel spurs and suffer no symptoms at all. Occasionally, heel pain is also associated with other medical disorders such as arthritis (inflammation of the joint), bursitis (inflammation of the tissues around the joint). Those who have symptoms may experience ?First step? pain (stone bruise sensation) after getting out of bed or sitting for a period of time. Pain after driving. Pain on the bottom of your heel. Deep aching pain. Pain can be worse when barefoot.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel pain often goes away on its own with home care. For heel pain that isn't severe, try the following. Rest. If possible, avoid activities that put stress on your heels, such as running, standing for long periods or walking on hard surfaces. Ice. Place an ice pack or bag of frozen peas on your heel for 15 to 20 minutes three times a day. New shoes. Be sure your shoes fit properly and provide plenty of support. If you're an athlete, choose shoes appropriate for your sport and replace them regularly. Foot supports. Heel cups or wedges that you buy in the drugstore often provide relief. Custom-made orthotics usually aren't needed for heel problems. Over-the-counter pain medications. Aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) can reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical Treatment
Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require surgery. If required, surgery is usually for the removal of a spur, but also may involve release of the plantar fascia, removal of a bursa, or a removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
deelsonheels
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.
What Is Mortons Neuroma
Overview
 Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve in the foot.Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain on the bottom of the foot. Treatments for Morton's neuroma include resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, ice packs, and operation. A neuroma is growth (benign tumor) that arises in nerve cells. A Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve located between the bones at the ball of the foot. The most common location of a Morton's neuroma is in either the second or the third spacing from the base of the big toe.
Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve in the foot.Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain on the bottom of the foot. Treatments for Morton's neuroma include resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, ice packs, and operation. A neuroma is growth (benign tumor) that arises in nerve cells. A Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve located between the bones at the ball of the foot. The most common location of a Morton's neuroma is in either the second or the third spacing from the base of the big toe.
Causes
The exact cause is unknown. Doctors believe the following may play a role in the development of this condition. Wearing tight shoes and high heels. Abnormal positioning of toes. Flat feet. Forefoot problems, including bunions and hammer toes. High foot arches. Morton neuroma is more common in women than in men.
Symptoms
The primary symptoms include sharp, shooting pain, numbness or paresthesia in the forefoot and extending distally into the toes, typically in the region of the third and fourth toes. Symptoms are aggravated with narrow toe box shoes or those with high heels. There is usually a reduction of symptoms when walking barefoot or wearing shoes with an appropriately wide toe box. Symptoms are also aggravated with shoes that are tied too tight.
Diagnosis
Metatarsal bones will be examined clinically, and often an x-ray will be taken to assess the particular case and ensure against other conditions, including fracture. When the foot is examined by a doctor, he may feel a characteristic ?click,? referred to as Mulder?s sign, and the interspaces between toe bones will often be tender. The doctor may put pressure on these areas to localize the site of pain and test for other conditions, including calluses or stress fractures. Range of motion tests will also be applied to rule out arthritis or joint inflammations. X-rays may be required to ensure there are no stress fractures or arthritis within the joints that join the toes to the foot. Tenderness in one or more metatarsal bones may imply a pre-stress fracture or stress-fracture. An ultrasound scan may be used to confirm diagnosis of Morton?s Neuroma, as x-ray will not detect the condition, (but can confirm that the bones are uninjured).
Non Surgical Treatment
Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for a neuroma. Analgesics may help. Inflammation it best eased via ice therapy and techniques or exercises that deload the inflammed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help. Your physiotherapist will use an array of treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include: ice, electrotherapy, acupuncture, deloading taping techniques, soft tissue massage and orthotics to offload the irritated nerve. One of the biggest factors in relieving pain may be changing or modifying your footwear. This may mean adding felt, foam or gel products to your shoe to help offload the area, or looking at avoiding tight fitting heels or shoes.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is occasionally required when the conservative treatment is not able to relieve your symptoms, particularly if you have had pain for more than 6 months. 80% of patients who require surgery report good results, with 71% of people becoming pain-free.
 Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve in the foot.Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain on the bottom of the foot. Treatments for Morton's neuroma include resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, ice packs, and operation. A neuroma is growth (benign tumor) that arises in nerve cells. A Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve located between the bones at the ball of the foot. The most common location of a Morton's neuroma is in either the second or the third spacing from the base of the big toe.
Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve in the foot.Morton's neuroma causes a "burning" sharp pain on the bottom of the foot. Treatments for Morton's neuroma include resting the foot, better-fitting shoes, anti-inflammation medications, ice packs, and operation. A neuroma is growth (benign tumor) that arises in nerve cells. A Morton's neuroma is a swollen, inflamed nerve located between the bones at the ball of the foot. The most common location of a Morton's neuroma is in either the second or the third spacing from the base of the big toe.Causes
The exact cause is unknown. Doctors believe the following may play a role in the development of this condition. Wearing tight shoes and high heels. Abnormal positioning of toes. Flat feet. Forefoot problems, including bunions and hammer toes. High foot arches. Morton neuroma is more common in women than in men.
Symptoms
The primary symptoms include sharp, shooting pain, numbness or paresthesia in the forefoot and extending distally into the toes, typically in the region of the third and fourth toes. Symptoms are aggravated with narrow toe box shoes or those with high heels. There is usually a reduction of symptoms when walking barefoot or wearing shoes with an appropriately wide toe box. Symptoms are also aggravated with shoes that are tied too tight.
Diagnosis
Metatarsal bones will be examined clinically, and often an x-ray will be taken to assess the particular case and ensure against other conditions, including fracture. When the foot is examined by a doctor, he may feel a characteristic ?click,? referred to as Mulder?s sign, and the interspaces between toe bones will often be tender. The doctor may put pressure on these areas to localize the site of pain and test for other conditions, including calluses or stress fractures. Range of motion tests will also be applied to rule out arthritis or joint inflammations. X-rays may be required to ensure there are no stress fractures or arthritis within the joints that join the toes to the foot. Tenderness in one or more metatarsal bones may imply a pre-stress fracture or stress-fracture. An ultrasound scan may be used to confirm diagnosis of Morton?s Neuroma, as x-ray will not detect the condition, (but can confirm that the bones are uninjured).
Non Surgical Treatment
Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for a neuroma. Analgesics may help. Inflammation it best eased via ice therapy and techniques or exercises that deload the inflammed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help. Your physiotherapist will use an array of treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include: ice, electrotherapy, acupuncture, deloading taping techniques, soft tissue massage and orthotics to offload the irritated nerve. One of the biggest factors in relieving pain may be changing or modifying your footwear. This may mean adding felt, foam or gel products to your shoe to help offload the area, or looking at avoiding tight fitting heels or shoes.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is occasionally required when the conservative treatment is not able to relieve your symptoms, particularly if you have had pain for more than 6 months. 80% of patients who require surgery report good results, with 71% of people becoming pain-free.
Are Shoe Lifts The Solution To Leg Length Imbalances
There are not one but two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies that you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter compared to the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the human brain senses the gait pattern and identifies some variance. Your body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch isn't grossly uncommon, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and normally doesn't have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this condition is very easily solved, and can eliminate many cases of back ache.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts . Most are low cost, generally being less than twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Upper back pain is the most prevalent ailment afflicting people today. Over 80 million people are affected by back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem that costs companies huge amounts of money yearly as a result of time lost and output. Innovative and improved treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of decreasing the economical influence this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these situations Shoe Lifts can be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of relieving any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic practitioners".
So that they can support the body in a well-balanced fashion, feet have got a crucial function to play. Inspite of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked region in the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that suitable posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes mainly undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this condition is very easily solved, and can eliminate many cases of back ache.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts . Most are low cost, generally being less than twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Upper back pain is the most prevalent ailment afflicting people today. Over 80 million people are affected by back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem that costs companies huge amounts of money yearly as a result of time lost and output. Innovative and improved treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of decreasing the economical influence this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these situations Shoe Lifts can be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of relieving any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous expert orthopaedic practitioners".
So that they can support the body in a well-balanced fashion, feet have got a crucial function to play. Inspite of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked region in the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts guarantee that suitable posture and balance are restored.
Podiatrists Choose Shoe Lifts For Leg Length Difference
There are actually two different kinds of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter than the other. As a result of developmental periods of aging, the brain senses the walking pattern and identifies some variation. The human body typically adapts by tilting one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch isn't grossly uncommon, doesn't need Shoe Lifts to compensate and normally won't have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this issue is simply fixed, and can eliminate quite a few cases of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality typically involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, typically being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Upper back pain is easily the most common health problem afflicting men and women today. Over 80 million people have problems with back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem that costs companies millions year after year due to lost time and productivity. New and superior treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economical impact this issue causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these situations Shoe Lifts can be of immense help. The lifts are capable of reducing any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless professional orthopaedic doctors.
To be able to support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, the feet have got a vital part to play. Despite that, it is sometimes the most neglected region of the body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that correct posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this issue is simply fixed, and can eliminate quite a few cases of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality typically involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, typically being under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Upper back pain is easily the most common health problem afflicting men and women today. Over 80 million people have problems with back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem that costs companies millions year after year due to lost time and productivity. New and superior treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of lowering economical impact this issue causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these situations Shoe Lifts can be of immense help. The lifts are capable of reducing any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless professional orthopaedic doctors.
To be able to support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, the feet have got a vital part to play. Despite that, it is sometimes the most neglected region of the body. Many people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that correct posture and balance are restored.
Caring For Calcaneal Spur

Overview
A heel spur is a hook of bone that can form on the heel bone of the foot. Heel spurs are associated with plantar fasciitis. Heel spurs can cause extreme pain in the rearfoot. The pain is most intense while standing or walking. What Causes Heel Spurs? Heel spurs develop as an abnormal growth in the heel bone due to calcium deposits that form when the plantar fascia stretches and pulls away from the heel. The plantar fascia is a ligament located at the bottom of your foot. This stretching of the plantar fascia is usually the result of flat feet or unusually high arches.
Causes
Heel spurs are exacerbated by an movements that stretch, twist or impact the plantar ligaments. Running, jumping, standing or walking on hard surfaces with unsupportive shoes, walking barefoot in sand are all activities that can activate heel spurs and plantar fasciitis. Obesity is another factor that increases stress to the plantar ligaments.

Symptoms
Most people think that a bone "spur" is sharp and produces pain by pressing on tissue, when in fact, these bony growths are usually smooth and flat. Although they rarely cause pain on their own, bone spurs in the feet can lead to callus formation as tissue builds up to provide added cushion over the area of stress. Over time, wear and tear on joints may cause these spurs to compress neighboring ligaments, tendons or nerves, thus injuring tissue and causing swelling, pain and tearing.
Diagnosis
A heel spur is often seen on X-ray as a bony protrusion, which can vary in size. However, because a Heel Spur only indicates increased load on the plantar fascia, and not pain, an ultra sound may be required to assess other actual cause of the heel pain such and may include checking to see if the plantar fascia is inflamed or degenerated.
Non Surgical Treatment
In some cases, heel spur pain may not be resolved through conservative treatment options. In those cases, cortisone injections may be used to reduce inflammation associated with the condition, helping to reduce discomfort. However, treatment options such as these must be discussed in detail with your physician, since more serious forms of treatment could yield negative side effects, such as atrophy of the heel's fat pad, or the rupture of the plantar fascia ligament. Although such side effects are rare, they are potential problems that could deliver added heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
Have surgery if no other treatments work. Before performing surgery, doctors usually give home treatments and improved footwear about a year to work. When nothing else eases the pain, here's what you need to know about surgical options. Instep plantar fasciotomy. Doctors remove part of the plantar fascia to ease pressure on the nerves in your foot. Endoscopy. This surgery performs the same function as an instep plantar fasciotomy but uses smaller incisions so that you'll heal faster. However, endoscopy has a higher rate of nerve damage, so consider this before you opt for this option. Be prepared to wear a below-the-knee walking cast to ease the pain of surgery and to speed the healing process. These casts, or "boots," usually work better than crutches to speed up your recovery time.